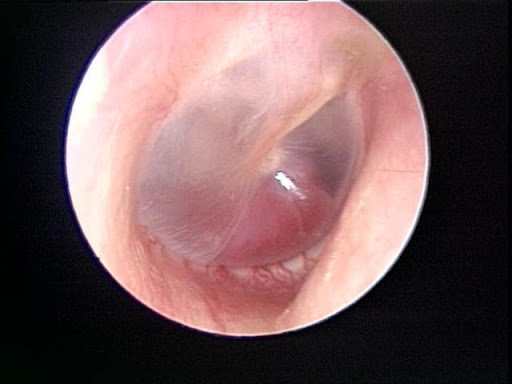
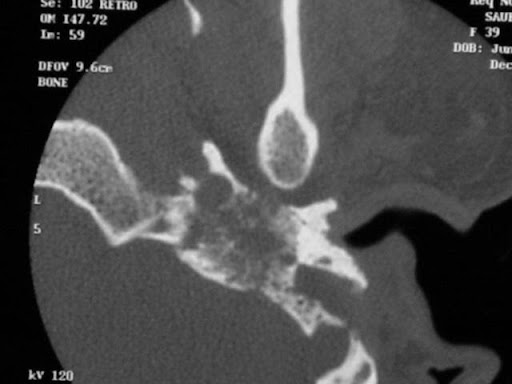
Surgery
The tumor can be removed using various skull base approaches, depending on the size of the tumor and level of hearing. Complete tumor resection usually results in cure, but large tumors may not be able to be removed completely. The surgery for smaller tumors consists of an out-patient procedure such as tympanoplasty with or without mastoidectomy. For larger tumors, an infratemporal fossa skull base resection which includes surgery on the neck may be needed. In these cases, in-patient hospitalization is needed for 1 to 2 days. Larger tumors can bleed significantly during surgery and may require blood transfusions. In these cases, the tumor is treated with a procedure called embolization prior to the surgery. During this procedure, a catheter is inserted into the blood vessels that go to the tumor and these vessels are plugged up in order to reduce bleeding during surgery. The hearing function can be saved in many cases, depending on the tumor size. The facial nerve function is usually preserved for small to medium size tumors. The swallowing, voice, and shoulder function is typically preserved but may be significantly affected after surgery for large tumors.